Introduction
Are you having trouble understanding the ins and outs of epoxy resin? You’re not alone. Epoxy resin is a reactive prepolymer and polymer compound with various industrial applications, from building construction to aerospace.
This comprehensive guide will make sure that by the end, you’ll know your epoxies as well as an industrial chemist! Are you ready to uncover this versatile material‘s secrets?
Key Takeaways
- Epoxy resin is a synthetic polymer compound with unique qualities such as high adhesive strength, durability, and potent chemical resistance.
- Depending on the presence of epoxide or hydroxyl groups, it can exist in different forms and is classified into types like glycidyl, novolac, and cycloaliphatic resins.
- Epoxy resin finds applications in various industries, including paints and coatings, adhesives, industrial tooling and composites, electrical systems and electronics, construction, and aerospace.
- When working with epoxy resin, it’s important to take safety precautions, such as wearing protective equipment and working in a well-ventilated area to minimize fume exposure.
Understanding Epoxy Resin
Epoxy resin is a versatile material used in various industries, known for its exceptional durability and strong bond strength.
Definition of epoxy resin
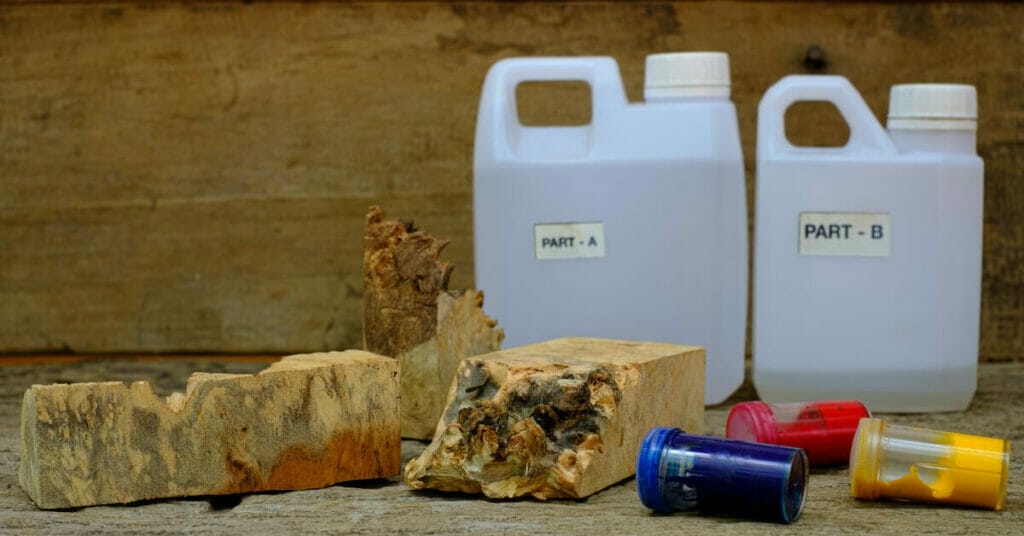
Epoxy resin is a synthetic polymer created from a reaction between epichlorohydrin (ECH) and bisphenol-A. This compound belongs to the family of reactive prepolymers, often called polyepoxides.
It features unique qualities such as high adhesive strength, durability, potent chemical resistance, and tough mechanical properties. At its core, it’s a molecule loaded with more than one epoxy group – this makes it convertible into a thermoset form when stimulated.
Technically speaking, an epoxy resin behaves like chemically reactive intermediates with at least two epoxide or hydroxyl groups in its structure, which lends it the ability to cross-link during the curing process – resulting in robust and durable material properties fit for various industrial applications.
Chemistry and composition of epoxy resin
Epoxy resin boasts a unique chemical composition that differentiates it from modern materials. As a molecule hosting multiple epoxy groups, this substance can morph into its thermoset form, providing unparalleled strength and durability.
At its core lies oxiranes; these underpin each epoxy resin’s defining traits – their robustness and distinctive thermosetting attributes. This polymer is defined by two essential components: epoxide or hydroxyl groups.
These reactive intermediates interact when mixed, triggering an impressive chemical reaction that births high-grade material with stellar mechanical properties and commendable resistance against chemicals.
Possessing a formidable adhesive strength, understanding the chemistry of epoxy resin becomes essential for wielding its capabilities across various industrial applications effectively.
Types of epoxy resin (glycidyl, novolac, cycloaliphatic, etc.)
Diving into the world of epoxy resins, we find a variety of subtypes, each with their unique properties and uses.
- Glycidyl Epoxy Resins: These are widely recognized and contain a glycidyl group. This group can be divided into three subcategories – glycidyl-ether, glycidyl-ester, and glycidyl-amine. The diversity within this classification expands the applications of epoxy resin.
- Novolac Epoxy Resins: Formed from phenol and formaldehyde, highly cross-linked structures known as phenolic novolac resins. They offer an excellent bonding system with superior heat resistance and mechanical properties.
- Cycloaliphatic Epoxy Resins: A special class falling under non-glycidyl epoxy resins, cycloaliphatic variations provide outstanding weather ability, dielectric properties, and resistance to ultraviolet light. Easy curing with catalysts also adds to their popularity.
Applications of Epoxy Resin
Epoxy resin finds applications in various industries, including paints and coatings, adhesives, industrial tooling and composites, electrical systems and electronics, construction, and aerospace.
Paints and coatings
Epoxy resin is widely used in the formulation of paints and coatings due to its excellent adhesive properties and durability. When applied as a coating, epoxy resin provides a protective layer that can withstand harsh environments, including chemicals and abrasion.
It also offers exceptional adhesion to various substrates such as metal, concrete, and wood. Additionally, epoxy resin coatings are known for their corrosion resistance and high gloss finishes, making them popular choices for industrial applications and decorative purposes alike.
With its ability to enhance the longevity of surfaces while providing an attractive finish, epoxy resin has become a go-to solution for domestic and commercial painting projects.
Adhesives
Epoxy resin is not only used for its superior adhesion, but it also serves as a key ingredient in various adhesive applications. Epoxy adhesives are widely known for their exceptional bonding abilities and versatility.
They can securely bond to various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. From construction projects to automotive manufacturing, epoxy adhesives are extensively used across industries due to their strong adhesive properties and durability.
One remarkable characteristic of epoxy adhesives is their ability to resist chemicals, extreme temperatures, and moisture. This makes them ideal for withstanding harsh conditions without compromising bond strength.
Additionally, epoxy adhesives offer excellent tensile and compressive strength thanks to the cross-linkage present in the cured resin.
The curing process of epoxy adhesives involves a chemical reaction between the epoxy resin and the curing agent. This reaction results in a hardening effect that strengthens the bond over time.
Once fully cured, epoxy adhesives provide long-lasting performance and reliable bonds that endure even under high stress or heavy loads.
Industrial tooling and composites
Epoxy resin plays a crucial role in industrial tooling and composites, providing strength, durability, and versatility for various applications. In tooling, epoxy resin is commonly used to create molds, master models, and prototypes due to its high mechanical strength and chemical resistance.
It allows for the precise replication of complex shapes and details. In composites, the epoxy resin acts as a binder that reinforces carbon fiber or fiberglass fibers to create lightweight yet strong materials utilized in industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Epoxy-based composites offer excellent resistance to heat and moisture while maintaining low shrinkage properties. This makes them ideal for creating components requiring exceptional performance under extreme conditions.
Electrical systems and electronics
Due to its exceptional properties, epoxy resin plays a crucial role in electrical systems and electronics. As an excellent electrical insulator, it protects components from short-circuiting and dust and moisture infiltration.
Additionally, epoxy resins provide strong adhesion, ensuring the various electronic parts stay securely bonded together. Their chemical resistance further enhances their suitability for these applications.
This versatile material is widely utilized across the electrical and electronics industries for its reliability and durability. Whether coating circuit boards or encapsulating delicate components, epoxy resin helps ensure the smooth functioning of our everyday gadgets and advanced electronic systems.
Construction and aerospace applications
Due to its exceptional properties, epoxy resin is widely used in construction and aerospace applications. In the construction industry, epoxy resin is utilized for various purposes, such as laminated wood, walls, roofs, and flooring.
Its ability to create strong bonds and provide durability makes it ideal for these structural applications. Additionally, epoxy resin finds extensive use in the aerospace industry.
It is the matrix phase in carbon-fiber composites used for aircraft structures, making them lightweight yet strong—moreover, epoxy resin is an adhesive for joining aircraft parts and performing repairs.
Safety Precautions and Health Risks
When working with epoxy resin, it is crucial to take appropriate safety precautions and be aware of the potential health risks associated with its use.
Handling and storage precautions
Working with epoxy resin requires certain precautions to ensure safety and proper handling. Here are some important guidelines to follow:
- Wear protective gloves throughout the entire resin handling process.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to minimize fume exposure, preferably with a respirator for added protection.
- Avoid direct skin contact with the resin or hardener by wearing long-sleeved clothing and pants.
- Use safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from accidental splashes or spills.
- Always mix epoxy resin components in the recommended ratios and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
- Store epoxy resin containers in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and sources of heat or ignition.
- Keep containers tightly sealed when not in use to prevent contamination or evaporation.
- Clean up spills immediately using appropriate cleaning materials, as epoxy resin can be slippery when spilled on surfaces.
- Dispose of unused or expired epoxy resin properly according to local regulations.
Potential health hazards and safety measures
Potential health hazards associated with epoxy resin exposure include:
- Skin irritation: Epoxy resin can cause skin irritation upon contact, leading to redness, itching, and inflammation.
- Respiratory issues: Overexposure to epoxy resin fumes or dust can lead to respiratory problems such as asthma, coughing, and difficulty breathing.
- Eye irritation: Contact with epoxy resin can irritate, including redness, itching, burning sensation, and watering.
- Allergic reactions: Some individuals may develop allergies to the chemicals found in epoxy resin products, leading to airway allergies and other allergic reactions.
- Chemical burns: Improper handling of epoxy resin can result in chemical burns on the skin or eyes.
- Use protective equipment: Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles/face shields, and a mask/respirator to minimize direct contact with the resin and reduce inhalation of fumes or dust.
- Adequate ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area or use exhaust fans and open windows/doors to prevent the buildup of fumes or dust particles.
- Handle carefully: Avoid splashes or spills using proper containers and handling techniques. Clean up any spills immediately using suitable absorbent materials.
- Store properly: Store epoxy resin products in a cool, dry place away from heat sources and direct sunlight. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for storage conditions.
- Follow usage instructions: Read the product label carefully and follow the manufacturer’s recommended dosage and mixing ratios.
- Take breaks: Limit prolonged exposure by taking regular intervals away from the work area to allow fresh air circulation.
- Seek medical advice if needed: If you experience persistent irritation or adverse health effects after exposure to epoxy resin, seek medical attention promptly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, epoxy resin is a versatile and durable thermosetting polymer that contains epoxide groups. It is widely used in various industries for its excellent chemical resistance, strong bond strength, and low porosity.
With its ability to adhere to different materials and quick curing time, epoxy resin has become essential in paints, adhesives, composites, electronics, and construction applications.
Understanding the definition of epoxy resin allows us to appreciate its wide-ranging uses and its important role in our daily lives.
FAQs
1. What is epoxy resin?
Epoxy resin is a synthetic polymer formed by a synthetic polymer epoxy compound and a hardening agent known as a curing agent. It is commonly used in various industries for its excellent adhesive properties, high strength, and resistance to chemicals and heat.
2. What are the main applications of epoxy resin?
Epoxy resin has a wide range of applications. It is commonly used as an adhesive in construction, electronics, automotive, and aerospace industries. It can also be used as a protective coating for floors, countertops, and other surfaces due to its durability and resistance to wear.
3. How does epoxy resin work?
When mixed with the epoxy compound and curing agent, they undergo a chemical reaction called curing or polymerization. This process transforms the liquid mixture into a solid material with strong bonding properties. The curing time can vary depending on factors such as temperature and formulation.
4. Is epoxy resin safe to use?
Epoxy resins are generally considered safe when handled properly according to manufacturer instructions. However, it’s important to take precautionary measures taking protective gloves and goggles while working with epoxy resin due to its potential skin irritation or allergic reactions caused by direct contact with uncured material. Proper ventilation should also be ensured during application processes to minimize inhalation risks from fumes emitted during curing.